10 Best Design Tools Shortlist
Here's my pick of the 10 best software from the 16 tools reviewed.
There is an overwhelming number of design tools on the market. So, how do you decide which design tool is right for you? You know you want to create and refine visual elements, layouts, and interactions for various digital and physical products, whether for websites, apps, graphics, or other design projects – and you need the right tool for the job. I've got you! In this post, I make things simple, leveraging my experience managing big, complex products, and being exposed to many design tools to bring you this curated list of the best design tools.
Why Trust Our Design Tool Reviews
We’ve been testing and reviewing design tools since 2021. As product designers ourselves, we know how critical and difficult it is to make the right decision when selecting software.
We invest in deep research to help our audience make better software purchasing decisions. We’ve tested more than 2,000 tools for different product management use cases and written over 1,000 comprehensive software reviews. Learn how we stay transparent & our design tools review methodology.
The Best Design Tools Comparison Chart
Here is a table that where you can compare all the tools we just covered in the overviews.
| Tools | Price | |
|---|---|---|
| SOLIDWORKS | Pricing upon request | Website |
| Altium Designer | Pricing available upon request | Website |
| Alibre Design | Pricing available upon request | Website |
| AVEVA E3D Design | Pricing available upon request | Website |
| Onshape | From $1,500/user/year | Website |
| Simcenter 3D | Pricing available upon request | Website |
| Solid Edge | From $110/month | Website |
| Fusion 360 | From $90/month | Website |
| NX CAD | Pricing available upon request | Website |
| IronCAD | Pricing available upon request | Website |

Compare Software Specs Side by Side
Use our comparison chart to review and evaluate software specs side-by-side.
Compare SoftwareHow to Choose Design Tools
With so many different design solutions available, it can be challenging to make decisions on what design tool is going to be the best fit for your needs.
As you're shortlisting, trialing, and selecting design tools consider the following:
- What problem are you trying to solve - Start by identifying the design tool feature gap you're trying to fill to clarify the features and functionality the design tool needs to provide.
- Who will need to use it - To evaluate cost and requirements, consider who'll be using the software and how many licenses you'll need. You'll need to evaluate if it'll just be the product design professionals, or the whole organization that will require access. When that's clear, it's worth considering if you're prioritizing ease of use for all, or speed for your design tool power users.
- What other tools it needs to work with - Clarify what tools you're replacing, what tools are staying, and the tools you'll need to integrate with, such as accounting, CRM or HR software. You'll need to decide if the tools will need to integrate together, or alternatively, if you can replace multiple tools with one consolidated design tool.
- What outcomes are important - Consider the result that the software needs to deliver to be considered a success. Consider what capability you want to gain, or what you want to improve, and how you will be measuring success. For example, an outcome could be the ability to get greater visibility into performance. You could compare design tool features until you’re blue in the face, but if you aren’t thinking about the outcomes you want to drive, you could be wasting a lot of valuable time.
- How it would work within your organization - Consider the software selection alongside your workflows and delivery methodology. Evaluate what's working well, and the areas that are causing issues that need to be addressed. Remember every business is different — don’t assume that because a tool is popular that it'll work in your organization.
Best Design Tool Reviews
You can use the simple overviews of the tools below to understand how each tool stands out from other design tools.
SOLIDWORKS is a software application that helps engineers and designers create 3D models of products and machines before building a physical prototype.
Why I picked SOLIDWORKS: The software's simulation capabilities help users understand how the design will behave under specific scenarios. This helps designers optimize the design mockup before moving to the production phase, which saves time and money during the development process. Additionally, SOLIDWORKS provides detailed visualizations of the simulation results so that users can identify problems and make design improvements.
SOLIDWORKS is a design software used in the manufacturing industry to create 3D models and simulations of products and machines. It offers a wide range of tools to create detailed and precise models. The software also allows easy collaboration between team members.
SOLIDWORKS Standout Features and Integrations
Features include parametric modeling, assembly modeling, drawing creation, simulation and analysis, CAM integration, product data management, add-ons, and customization.
Integrations include Fishbowl, Makersite, Total ETO, Genius ERP, ImageSite, MRPeasy, Kenesto, Global Shop Solutions, Valispace, Epicor CPQ, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Excellent rendering and visualization capabilities
- Compatible with a wide range of file formats
- Supportive user community
Cons:
- Expensive for small businesses and individuals
- Requires high-end hardware
Altium Designer helps designers create the physical layout of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and the schematics and other documentation needed for manufacturing.
Why I picked Altium Designer: The software performs real-time design rule checking (DRC) during the PCB layout process. The software will automatically check the design against predefined design rules and constraints. In addition, Altium Designer's advanced 3D visualization tools allow designers to visualize their designs in 3D and detect potential mechanical collisions, ensuring that the PCB layout fits appropriately within the mechanical enclosure.
The software has an intuitive interface and comprehensive tools for creating and testing electronic designs, which makes it ideal for various industries, including aerospace, defense, telecommunications, and consumer electronics.
Altium Designer's powerful features and advanced simulation tools make it an excellent tool for creating high-quality PCBs.
Altium Designer Standout Features and Integrations
Features include schematic capture, PCB layout, 3D PCB design, mixed-signal circuit simulation, signal integrity analysis, power integrity analysis, thermal analysis, design rules checking (DRC), design for manufacturing (DFM), bill of materials (BOM) management, ECAD/MCAD collaboration, library management, design reuse and variant management, team collaboration, and design data management.
Integrations include OpenBOM, Arena PLM, Altium’s PDN Analyzer, TASKING, JTAG Maps™, Xilinx, AllSpice, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Easy-to-navigate interface
- Plenty of tools for design documentation and schematic capture
- Large library of pre-built components and design templates
Cons:
- Some users report bugs and glitches
- Limited file compatibility
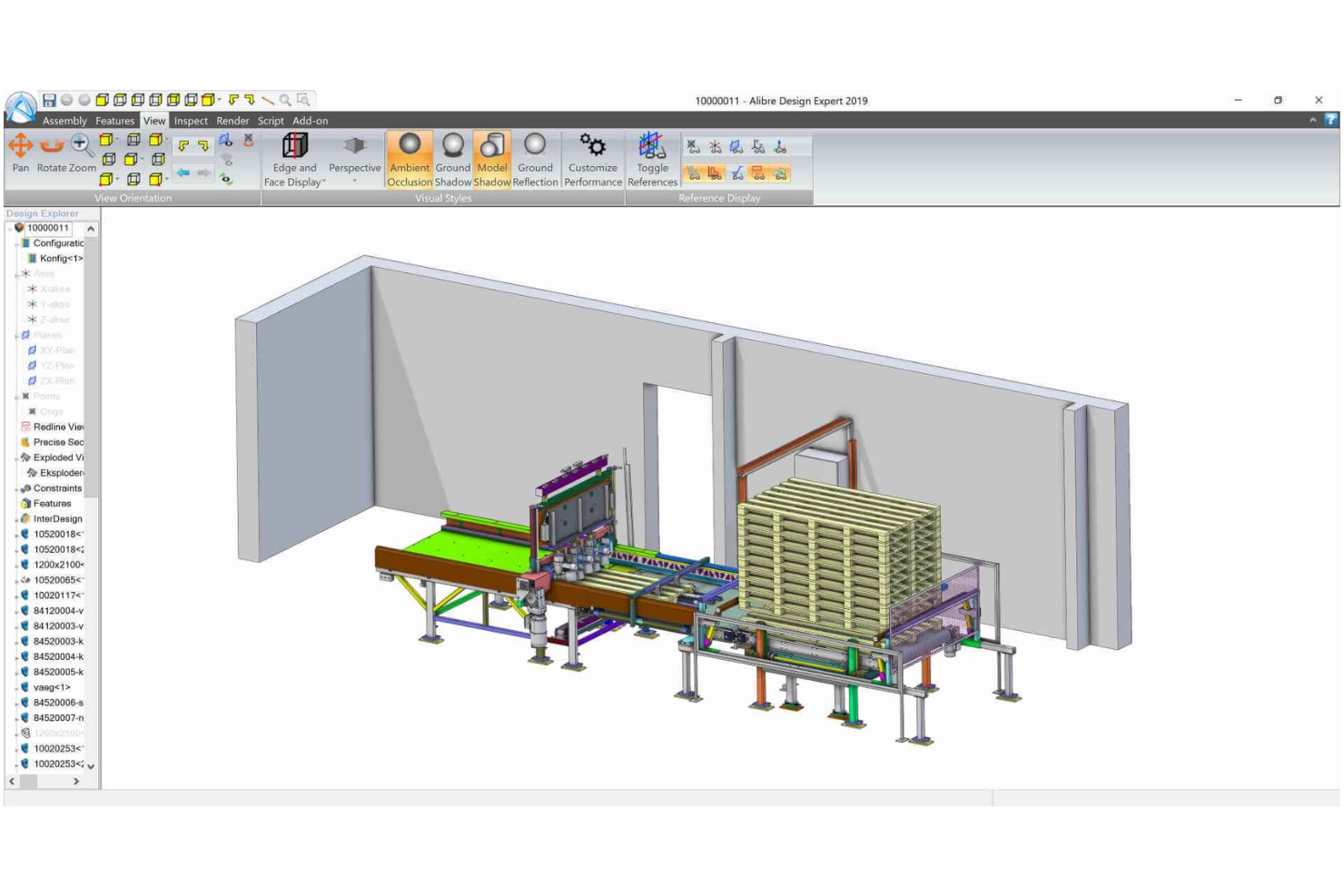
Alibre Design is a 3D CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software that helps engineers, designers, and manufacturers create prototypes, wireframes, product designs, and other mechanical parts.
Why I picked Alibre Design: The software offers a real-time physics engine, which allows users to simulate the behavior of parts and assemblies in real-world conditions. It lets users test how their designs will function in the real world, including the movement of parts, and the impact of gravity and other forces. This helps users identify potential design flaws or areas for improvement before manufacturing or prototyping, saving time and resources in the long run.
Alibre Design is well-suited for various use cases, including product design, mechanical engineering, prototyping, and more. It is beneficial for small businesses, startups, and individual designers who need powerful CAD software at an affordable price. Its ease of use and accessibility make it a good choice for those new to 3D modeling and design, while its advanced features and simulation tools make it a powerful tool for more experienced users.
Alibre Design Standout Features and Integrations
Features include 3D design, sheet metal, assemblies, drawings, scripting, part families, rendering, CAM, and file formats.
Integrations include FEMdesigner AD, SimWise, SimLab Composer, Keyshot, Desktop EDA, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Affordable pricing compared to other CAD software
- User-friendly interface and intuitive tools
- Helpful tutorials and resources for new users
Cons:
- Customer support can be slow
- May not be suitable for designs that require extensive collaboration
AVEVA E3D Design is a 3D modeling software used in engineering and construction projects. It allows users to create digital models of various objects and structures, such as buildings, bridges, or oil rigs, and simulate their behavior in real-world environments.
Why I picked AVEVA E3D Design: The design platform integrates with laser scanning technology, enabling users to capture as-built conditions in 3D and incorporate them into the design process. This allows for more accurate and efficient designs, as well as better communication between the design and construction teams.
Product designers in the engineering, procurement, and construction industries use AVEVA E3D Design to design complex industrial plants such as oil refineries, chemical plants, and power plants. It enables designers to collaborate in real time, creating a highly detailed and accurate 3D model of the plant.
AVEVA E3D Design Standout Features and Integrations
Features include a unified design environment, mobile app, 3D modeling, clash detection, rule-based design, integrated materials management, collaboration tools, integrated analysis, and visualization.
Integrations include AVEVA Intelligence, AVEVA Enterprise Resource Management, Intratech's Smart 3D PDF Exporter, AVEVA Unified engineering, Visual KPI, AVEVA NET, AVEVA PDMS, AVEVA Pipe Stress, AVEVA Laser Modeller, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Robust 3D modeling capabilities
- User-friendly interface
- Large user community and resources
Cons:
- Steep learning curve
- Limited customizations
Onshape is a computer-aided design (CAD) software that helps professionals create virtual models of products and machines in a collaborative, cloud-based environment.
Why I picked Onshape: A cool thing about Onshape is its real-time collaboration features, which allow multiple users to work on the same design simultaneously. While working, users don't have to worry about version control or conflicts between different versions of a design. Onshape also includes built-in messaging and commenting tools that allow team members to communicate and share feedback directly within the software.
Onshape is ideal for design teams distributed across different locations, as it enables real-time collaboration and sharing of design data without the need for expensive hardware or software installations. In addition, it is beneficial for industries that require collaboration and agility, such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
Onshape Standout Features and Integrations
Features include simulation, PCB Studio, Render Studio, Onshape-Arena Connection, data management, collaboration, version and release management, parts, assemblies, drawings, bill of materials, configurations, analytics, integrations, support, security, and frames.
Integrations include OnScale, Cadasio, Xometry, Monarch, Flatter Files, OnelPM, Phi, Arena, SimScale, OpenBOM, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Highly scalable and flexible
- Includes automatic software updates
- Large library of 3D models and parts
Cons:
- Limited offline functionality
- Limited support for simulation and analysis tools
Simcenter 3D is a design software that helps engineers create digital models of their products and run simulations to test their performance, durability, and safety.
Why I picked Simcenter 3D: I picked Simcenter 3D because of its ability to perform topology optimization. The tool allows engineers to input their design requirements and constraints, automatically generating an optimized design that meets those requirements. This process can lead to significant weight reduction and improved performance of a product while still maintaining its strength and structural integrity.
The software is primarily used in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing industries, where engineers need to design and optimize complex products with a wide range of performance requirements. It is ideal for engineers who need to perform advanced simulations and analyses across multiple engineering disciplines, such as structural, thermal, fluid, and electromagnetic.
Simcenter 3D Standout Features and Integrations
Features include structural analysis, structural dynamics, acoustic simulation, durability and fatigue analysis, motion simulation, electromagnetics simulation, materials engineering, thermal analysis, multiphysics, additive manufacturing build simulation, and data management.
Integrations include Siemens NX, SolidWorks, CATIA, Pro/ENGINEER, ANSYS, Abaqus, Siemens Polarion, Siemens Simcenter Testlab, Siemens NX AM, Siemens Simcenter Amesim, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Used in a variety of industries
- Advanced automation and optimization tools
- Has a powerful meshing capability
Cons:
- Limited learning resources
- Occasional downtimes
Solid Edge helps to create designs for products and machines, such as cars, airplanes, and household appliances.
Why I picked Solid Edge: The best part about Solid Edge is its ability to create and edit models using a combination of both parametric and direct modeling techniques. This helps designers make changes to the design without worrying about the constraints and relationships between different features.
Additionally, you can perform finite element analysis (FEA) on designs, which helps test and optimize the products for performance and durability before they are built. Also, its synchronous technology will help you edit 3D models, regardless of their original design software or file format. This means you won't have to start from scratch or spend hours manually adjusting individual features.
Solid Edge Standout Features and Integrations
Features include 2D drawing, 3D imaging, animation, CAD tools, collaboration tools, compliance management, component library, continuous modeling, data import/export, data synchronization, data visualization, design analysis, design management, document management, and dynamic modeling.
Integrations include Google Drive, Dropbox Business, OneDrive, Box, Global Shop Solutions, Smap3D Plant Design, Smap3D ScanToCAD, BoltsEtAl, SimLab Soft, HOOPS Exchange, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Synchronous technology allows fast design modifications
- Natively integrates with Siemens PLM software ecosystem
- Intuitive workflow and interface
Cons:
- Limited third-party software integrations
- Steep learning curve for beginners
Fusion 360 helps small and medium-sized businesses to design, simulate, render, and fabricate their ideas. You can use it to create anything from a small gadget to a large industrial machine. The software is available for both iOS and Android.
Why I picked Fusion 360: I picked Fusion 360 for its generative design functionality. It uses advanced algorithms to generate optimized designs based on user-specified design criteria and constraints. For example, you can set parameters such as material type, manufacturing constraints, etc., and the tool will explore thousands of possible design iterations.
If you are an engineer, industrial designer, or architect, Fusion 360 can be your ally for creating and testing designs in a 3D digital environment. Also, it provides CAD, CAM, and CAE tools in a single software package, which makes it great for both product designing and engineering.
Additionally, its real-time collaboration features make it easy for team members to work on the same design together, regardless of location. This enables faster decision-making and improved designs.
Fusion 360 Standout Features and Integrations
Features include 3D modeling and design, interactive assemblies, sheet metal part creation, automation tools, plugins, electronics and PCB engineering tools, SPICE simulation, hierarchical schematic capture, cloud collaboration and data management, photo-realistic rendering and documentation, FEA verification, test, and simulation.
Integrations include Makersite, OpenBOM, AWS Secrets Manager, Causeway Flow, Bantam Tools, HSMWorks, ElectricalOm, Autodesk A360, SimLab Composer, FeatureCAM, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Affordable pricing options
- Offers several online learning resources
- Cloud-based tool
Cons:
- Limited offline functionality
- Requires a reliable internet connection
NX CAD is a computer-aided design (CAD) software that helps users create, modify, and optimize complex designs for automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
Why I picked NX CAD: The tool stands out due to its open architecture, which supports a wide range of file formats, making it easy to collaborate with other design software. It also integrates with product lifecycle management (PLM) systems so that you can manage your design data, documents, and processes in one place.
This tool is primarily for large organizations in the manufacturing industry to design and optimize complex products and machinery. The advanced surface modeling and assembly modeling capabilities ensure that designers can create detailed models.
NX CAD Standout Features and Integrations
Features include 3D design validation, automation design, drafting and documentation, industrial design and styling, industrial electrical design, knowledge reuse, mechatronic concept design, and product modeling.
Integrations include Teamcenter, Simcenter, Tecnomatix, Siemens NX CAM, ANSYS, Abaqus, CATIA, SolidWorks, AutoCAD, Inventor, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Highly customizable interface
- Supports collaboration and teamwork
- Exhaustive range of tools
Cons:
- Complicated 2D drawing tool
- Requires high-performance computer
IronCAD is a 3D CAD software that uses a drag-and-drop approach to modeling. It allows users to quickly and easily create complex designs by manipulating pre-existing shapes and objects.
Why I picked IronCAD: IronCAD's TriBall interface lets users manipulate objects in 3D space using an intuitive drag-and-drop feature. The software's 'SmartSnap' technology ensures that objects are accurately aligned and positioned. IronCAD's LiveLinking feature also allows users to link their designs to other software applications, such as analysis or simulation tools, and make real-time changes that update across all linked applications.
Mechanical engineers, product designers, and manufacturers primarily use IronCAD to create 3D models of complex mechanical systems and products. Its ability to work with solids and surfaces makes it a popular choice for engineers who need to perform complex simulations and analyses on their designs.
IronCAD Standout Features and Integrations
Features include 2D drawing, 3D imaging, animation, annotations, bill of materials management, CAD tools, collaboration tools, component library, data import/export, design analysis, document management, modeling and simulation, project management, and reporting and analytics.
Integrations include Design Data Manager, SprutCAM, CADENAS, Rhinoceros, DOSCH DESIGN, 3Dconnexion, TraceParts, Renishaw, NCG CAM Solutions, and other software options.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Supports a wide range of file formats
- Built-in rendering capabilities
- Flexible modeling options
Cons:
- Limited documentation and user community
- Limited animation and motion capabilities
Other Design Tools
Here are a few more options that didn’t make the best design tools list:
- KeyCreator
Best for dynamic editing of designs
- Mastercam
Best for precision machining and CNC programming
- CATIA
Best for creating large and complex designs
- Tebis
Best for automotive, aerospace, mold and die, and industrial design
- Inventor
Best for creating digital mockups of products and parts in a virtual environment
- CircuitStudio
Best for designing printed circuit boards (PCBs)
Related Product Management Software Reviews
If you still haven't found what you're looking for here, check out these other related tools that we've tested and evaluated:
- Best Product Management Tools
- Best Product Planning Software
- Best UX Design Tools
- Best Product Development Software
- Best Idea Management Software
- Best Heatmap Software
Selection Criteria for Design Tools
Selecting design tools requires a nuanced understanding of both the functionality these platforms offer and how well they meet specific use cases that are critical to the design process. Through personal trials and extensive research, I've developed a set of weighted criteria to evaluate design tools, ensuring they not only meet generic requirements, but also offer unique value to their users.
Core Design Tool Functionality (25% of total weighting score): To be considered for inclusion on my list of the best design tools, the solution had to support the ability to fulfill common use cases. These include:
- Vector editing and drawing for scalable graphics
- Collaboration tools for team-based projects
- Asset management for organizing and reusing design elements
- High-fidelity prototyping for interactive user experience testing
- Responsive design features for cross-platform compatibility
Additional Standout Features (25% of total weighting score): Standout features distinguish a tool from its competitors by providing innovative solutions to complex design challenges. This evaluation looks for unique and advanced functionalities that enhance the creative process and offer users a competitive edge in their design work. Such functionalities can include:
- Unique tools for AI-driven design suggestions, enhancing creativity beyond basic functionalities.
- Advanced integration capabilities with other software, streamlining workflows across different platforms.
- Customizable user interfaces that adapt to specific project needs or designer preferences, offering a more personalized design experience.
- Innovative prototyping features that allow for more dynamic user experience testing, such as VR integration or real-time user interaction analytics.
Usability (10% of total weighting score): Usability is key to ensuring that designers can leverage the full power of a tool without a steep learning curve, making it an essential factor in tool selection. This criterion assesses:
- A balance between powerful features and a user-friendly interface, ensuring that new users can navigate the tool with ease.
- Design interfaces that are clean and uncluttered, with intuitive drag-and-drop functionalities for ease of use.
Onboarding (10% of total weighting score): Effective onboarding is critical for users to quickly realize the value of a design tool, especially in fast-paced work environments. This evaluation focuses on the availability and quality of educational resources, templates, and support offered to new users, ensuring they can efficiently learn and leverage the tool’s features from day one. I look for:
- Comprehensive training materials, such as video tutorials, interactive product tours, and detailed documentation, to help new users get up to speed quickly.
- Ready-to-use templates and project presets that allow new users to start creating designs with minimal setup time.
Customer Support (10% of total weighting score): Reliable customer support is a safety net for users, providing assistance when they encounter issues or have questions. This criterion ensures that users have the necessary support to overcome any obstacles in their design process by evaluating:
- Access to a knowledgeable and responsive support team through multiple channels, including live chat, email, and phone.
- A rich online community or forum where users can exchange tips, tricks, and advice.
Value For Money (10% of total weighting score): Value for money is not just about the cost but also return on investment in terms of features, efficiency gains, and output quality. This evaluation compares the pricing and subscription models of different tools against their offered functionalities and benefits, ensuring users receive maximum value for their investment. This includes:
- Competitive pricing models that offer good value based on the features and capabilities provided.
- Flexible subscription options that cater to different user needs and budget constraints.
Customer Reviews (10% of total weighting score): Customer reviews offer invaluable insights into a tool's real-world performance, user satisfaction, and potential drawbacks. This criterion leverages feedback from a broad user base to gauge overall satisfaction levels to guide potential buyers in making informed decisions. It assesses:
- High ratings for ease of use, feature set, and customer support, indicating overall satisfaction with the tool.
- Positive feedback on the tool's ability to streamline the design process and improve team collaboration.
This comprehensive approach ensures that users can select design tools that are capable of supporting the full spectrum of design activities, from initial concept through to final prototype, in a way that maximizes creativity, efficiency, and collaboration.
Trends in Design Tools for 2024
For design tools, 2024 has seen some significant advancements and shifts that reflect the evolving needs of product design professionals. This analysis aims to highlight these new trends, focusing on functionality improvements and adaptations and how they address specific needs within the product design landscape.
Trends in Design Tools and Technology
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies into design tools has been a standout trend. These features are rapidly evolving to offer predictive design suggestions, automate routine tasks, and facilitate more intuitive user experiences. For instance, AI-driven auto-correction and enhancement features in image editing tools have significantly reduced manual editing time, showcasing a shift towards more intelligent, assistive design technologies.
- Collaboration and Remote Work Features: Enhanced collaboration features have become a mainstay in design tools, responding to the global shift towards remote work. Real-time co-editing, cloud-based file sharing, and integrated communication tools have seen substantial updates, making teamwork more seamless and efficient. This evolution mirrors the growing demand for tools that support a distributed workforce while maintaining project cohesion.
- High-Fidelity Prototyping Capabilities: There's been a marked increase in the sophistication of prototyping features within design tools. The ability to create more realistic and interactive prototypes—complete with animations, transitions, and user interaction simulations—has become more advanced. These updates reflect the need for designers to more accurately visualize and test user experiences before final development stages.
- Sustainability and Inclusivity Features: A novel and somewhat unusual trend is the incorporation of features aimed at promoting sustainability and inclusivity in design. Tools now offer guidelines and checks for creating designs that are accessible to a wider range of users and have a lower environmental impact. This functionality is emerging in response to a growing recognition of the social and environmental responsibilities of design work.
Evolving and In-Demand Features
- Cloud-Based and Cross-Platform Accessibility: Cloud-based design tools and those offering cross-platform compatibility are also becoming increasingly important in the product design space. This reflects the need for flexibility in accessing and working on projects across different devices and operating systems, catering to the modern designer's mobile and versatile work style.
Features Becoming Less Important
- Overly Complex Feature Sets: There's a noticeable move away from tools overloaded with complex features that have steep learning curves. Simplicity, efficiency, and ease of use are becoming key, as designers seek tools that allow them to focus more on creativity and less on navigating cumbersome software interfaces.
The landscape of design tools in 2024 is one of rapid innovation and adaptation, driven by the evolving needs of product design professionals. As these trends continue to unfold, they not only reflect the current priorities and challenges within the design community, but also signal the direction of future software development in the field.
What are Design Tools?
Design tools encompass a variety of software used to create, edit, and optimize visual elements in design projects. These tools range from graphic design software to user interface design tools, providing designers with the functionalities they need to bring their creative visions to fruition.
The essential features these design tools offer are drawing and painting tools, layers, image editing, typography, vector editing, exporting to different file formats, and collaboration tools. Graphic design, web design teams, and other creative professionals use these tools to communicate their ideas visually.
Features of Design Tools
Design tools play a crucial role in the creative process, serving as the bridge between a designer's vision and the final product. These tools not only allow for the initial creation of design concepts, but also support their visualization and refinement through to the finished prototype. As such, selecting the right design tools with the right features can dramatically enhance the efficiency and quality of the design process. Here are some key features to look for when choosing design tools to facilitate these critical stages of design development.
1. Intuitive User Interface: A tool that is easy to navigate and understand. This is essential because it allows designers to focus more on their creative process rather than spending time learning how to use the software.
2. Vector Editing Capabilities: Offers precise control over design elements. Vector editing is vital for creating scalable designs that maintain their quality at any size, which is crucial for a wide range of applications.
3. Collaboration Features: Enables real-time collaboration with team members. Collaboration features are important for a seamless workflow, allowing multiple team members to work on the same project simultaneously and share feedback instantaneously.
4. Comprehensive Asset Library: Provides a wide range of pre-made assets. Having access to a vast library of assets can significantly speed up the design process by providing ready-to-use elements that can be customized as needed.
5. High-fidelity Prototyping: Allows for the creation of interactive prototypes. High-fidelity prototyping is crucial for testing and refining user experiences, ensuring the final product is both functional and user-friendly.
6. Version Control: Tracks changes and revisions over time. Version control is indispensable for managing multiple iterations of a design, enabling designers to explore different directions without losing previous work.
7. Compatibility with Other Tools: Ensures seamless workflow integration. Being able to integrate and exchange files with other design and productivity tools is crucial for maintaining an efficient workflow across different stages of the design process.
8. Customization Options: Offers the ability to tailor the workspace and tools to one's needs. Customization enhances efficiency by allowing designers to set up their workspace in a way that best suits their workflow and project requirements.
9. Responsive Design Features: Facilitates the creation of designs that work on multiple devices and screen sizes. This feature is increasingly important in a world where digital content is accessed from a wide variety of devices.
10. Extensive Export Options: Supports a wide range of file formats for output. Having multiple export options is essential for delivering the final product in the required format, whether for print, web, or app development.
These features not only help in creating visually appealing designs, but also ensure that the designs can be effectively tested, refined, and delivered across various platforms and media. The goal is to choose tools that both meet the current needs of a project and support the evolving demands of future projects, making the design process as smooth and efficient as possible.
Benefits of Design Tools
By leveraging powerful design tools, users can streamline their workflows, enhance collaboration, and bring their creative visions to life with greater efficiency and precision. Here are five primary benefits of design tools that are particularly compelling for potential buyers in the market:
1. Increased Efficiency: Design tools come with features like templates, drag-and-drop interfaces, and automation that significantly reduce the time and effort required to produce high-quality designs, allowing businesses to deliver projects faster and with less manpower.
2. Enhanced Collaboration: Modern design tools often include real-time collaboration features, enabling team members to work together seamlessly, regardless of their physical location, which can lead to better communication, faster decision-making, and a more cohesive final product.
3. Improved Accuracy and Consistency: Design software provides tools for precise editing and layout options, as well as style guides and asset libraries, which help maintain consistency across a brand's visual identity, enhancing professional appearance and brand recognition.
4. Scalability: With design tools, organizations can easily scale their design efforts up or down based on current needs without significant changes to their workflow or additional investment in new software, making it easier to adapt to project demands and market changes.
5. Cost Savings: By enabling in-house teams to produce professional-level designs, organizations can lower their reliance on costly external design agencies and freelancers, leading to significant long-term savings on project and operational costs.
The adoption of design tools offers compelling advantages for both individual users and organizations. For potential design tool buyers, understanding these benefits is key to making informed decisions that will enhance their operational capabilities and competitive edge in the marketplace.
Costs & Pricing for Design Tools
Design tools typically offer a range of plans to cater to different user needs, from individuals and small teams to large enterprises. These plans vary both in price and in the features and capabilities they provide, making it crucial for buyers to understand what each plan offers and how it aligns with their specific requirements.
Below is a breakdown of the common plan options and pricing for design tools, designed to help demystify the selection process for those new to using such software.
Plan Comparison Table for Design Tools
| Plan Type | Average Price | Common Features |
|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | Basic design features, limited templates, essential tools, single-user access, basic support |
| Individual | $10 - $30/month | Advanced design capabilities, more templates, cloud storage, premium assets, email support |
| Professional | $30 - $60/month | Collaboration tools, team management, unlimited cloud storage, priority support, advanced analytics |
| Business | $60 - $100+/month | Advanced security features, SSO, custom branding, dedicated account manager, enterprise support |
| Enterprise | Custom Pricing | Custom integrations, full feature access, on-premise deployment options, 24/7 support, training sessions |
When selecting a plan, software buyers should consider the scale of their projects, the size of their team, and the specific features they need to effectively execute their design tasks. It's essential to balance cost against functionality to ensure that you choose a plan that not only fits your budget, but also adequately supports your design processes and goals.
Design Tools Frequently Asked Questions
Here are a few popular questions answered for your convenience!
How do I choose a design tool?
Here are some factors to consider when choosing a design tool:
- Purpose: Understand the purpose for which you need a design tool, as different tools have different purposes, such as graphic design, web design, or user experience/UI design. Some popular graphic design tools are Canva, Adobe Illustrator, Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Creative Cloud, and Figma.
- Compatibility: Check the compatibility of the design tool with your operating system and other software.
- Features: Make sure the tool offers all the essential features required to make designs.
- Price: Design software varies in price, so determine your budget while selecting a design tool.
- User Interface: A complex interface can hamper productivity and creativity. Look for tools with an easy and intuitive interface.
- Customer support and community: Look for design tools that offer good customer support and a supportive community. This can be helpful if you run into any issues while using the tool.
What are the key features of design tools?
The key features of design tools include:
- Drawing and editing tools: Design software offers drawing and editing tools, such as pen, brush, eraser, shape tools, and text tools.
- Layers: This feature helps designers create and separate different design elements.
- Exporting and sharing options: This feature helps users share files and export designs in different formats.
- Collaboration tools: These tools help multiple users work on the same design, making collaborating and sharing information easier.
- Customization options: This includes a variety of customization options, such as the ability to add custom brushes, fonts, or other assets.
What other product-building software should I use?
Here are some other product-building software you might want to try:
Use Design Tools To Bring Your Ideas To Life
Design tools help businesses transform their product ideas into concrete representations. They also facilitate communication between team members and ensure everyone is working towards the same vision. With that in mind, I hope this top 10 list helped you find the right design tools for your team.
If you’d like to learn more about product management and design software, sign up for our newsletter.