In today's competitive business landscape, it is essential for companies to consistently enhance their value-creation processes to remain relevant and competitive. One approach that businesses can take is Value Chain Analysis (VCA).
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what VCA is, its importance in business strategy, its components, and how to conduct it. We will also look at the challenges and limitations that businesses face while implementing it, and some successful case studies. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of VCA and how it can benefit your organization.
Introduction To Value Chain Analysis
The concept of VCA was introduced by Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter in 1985 in his book, Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. The primary objective of VCA is to identify value-added activities in a company's operations that can be optimized to improve efficiency, cost savings, profit margins, customer value, and competitiveness.
VCA is a powerful tool that enables businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their operations, from the sourcing of raw materials to the delivery of final products to customers. By breaking down the various components of their operations, businesses can identify areas where they can optimize resources, lower costs, and create the most value.
What is Value Chain Analysis?
Straightforwardly put, Michael Porter’s VCA is an analytical framework that helps businesses gain a deep understanding of their operations by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable components. By doing this, the goal is to identify cost drivers and areas where they can optimize their workflows as well as outputs while creating more value overall.
For example, a business that manufactures and sells clothing may use VCA to analyze its operations. The value chain for this organization would include business activities such as sourcing of raw materials, designing and production of clothing, marketing and sales, and distribution to customers. By analyzing each of these activities, the business can identify areas where it can optimize resources and create more value.For instance, the business may find that it can reduce costs by sourcing raw materials from a different supplier or by using more efficient production methods. Alternatively, the business may identify new marketing and sales channels that can help it reach more customers and increase its revenue.
Importance of Value Chain Analysis in Business Strategy
VCA is crucial in business strategic planning as it enables organizations to recognize their core competencies and differentiation advantages. It also helps businesses to understand how they fit in the broader value system and identify areas where they can add value to the distribution or supply chain.
By conducting VCA, businesses can identify areas where they can differentiate themselves from competitors create a competitive advantage and become more lean. For example, a business that specializes in sustainable and eco-friendly products may use VCA to identify areas where it can optimize its operations to reduce its carbon footprint, pricing, and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
Overall, VCA is a valuable tool for businesses looking to improve their operations and product design to reduce costs and create a cost advantage. By breaking down their operations into small components and analyzing each activity, businesses can identify areas for improvement and optimize their resources to gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Components Of A Value Chain
A value chain is a series of activities that a company performs to deliver a valuable service or product to its customers. It is made up of two primary components; primary activities and support activities.
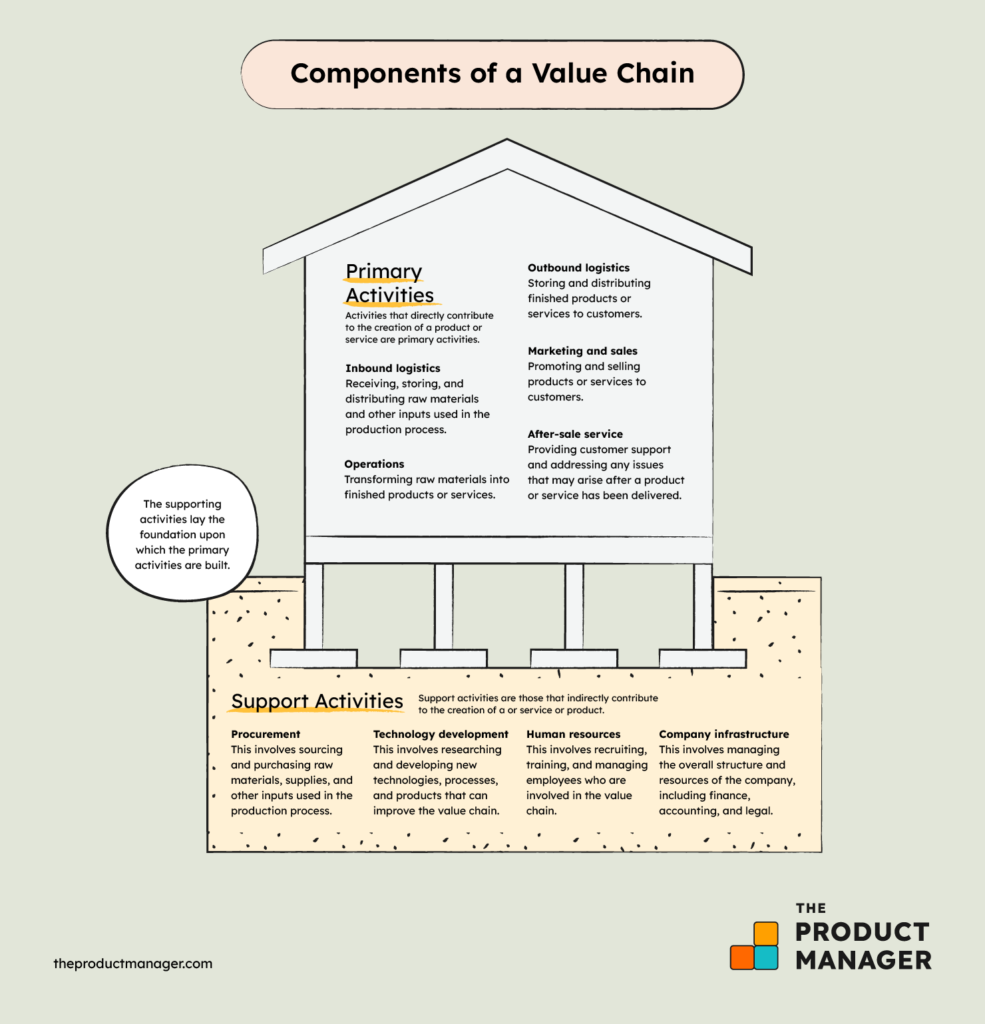
Primary Activities
Activities that directly contribute to the creation of a product or service are primary activities. They include:
Inbound logistics
This involves receiving, storing, and distributing raw materials and other inputs used in the production process.
Operations
This involves transforming raw materials into finished products or services.
Outbound logistics
This involves storing and distributing finished products or services to customers.
Marketing and sales
This involves promoting and selling products or services to customers.
After-sale service:
This involves providing customer support and addressing any issues that may arise after a product or service has been delivered.
Support Activities
Support activities are those that indirectly contribute to the creation of a or service or product. These include:
Procurement
This involves sourcing and purchasing raw materials, supplies, and other inputs used in the production process.
Technology development
This involves researching and developing new technologies, processes, and products that can improve the value chain.
Human resources
This involves recruiting, training, and managing employees who are involved in the value chain.
Company infrastructure
This involves managing the overall structure and resources of the company, including finance, accounting, and legal.
The Role of Interrelationships in the Value Chain Model
The interrelationships between different activities are critical as each activity impacts the overall value-creation process. For example, if the inbound logistics process is inefficient, it can lead to delays in production and delivery, which can negatively impact customer satisfaction. Similarly, if the marketing and sales process is ineffective, it can lead to low sales and revenue. Companies that identify, understand, and optimize these relationships between different activities in the value chain tend to operate more efficiently, create more value, and are more competitive.By focusing on improving each component of the value chain, companies can create a competitive advantage and deliver more value to their stakeholders, customers, and shareholders. Overall it can lead to increased customer loyalty, higher profits, and long-term success.
How To Conduct Value Chain Analysis
Conducting a Value Chain Analysis (VCA) is an essential process for identifying areas for differentiation to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and add value. It involves four critical steps:
Step 1: Identify Activities within the Value Chain
The first step in conducting Porter's value chain analysis is to identify all the activities involved in a company’s value chain, both primary and support. Primary activities are directly involved in the creation and delivery of a product or service, while support activities enable primary activities to function efficiently. Mapping these activities allows businesses to have a bird's eye view of their operations.
For example, in a manufacturing company, primary activities may include logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and after-sales service. Support activities may include technology development, procurement, human resource management, and infrastructure.
Step 2: Analyze the Importance of Each Activity
The next step is to determine which activities are crucial to the value creation process by analyzing their costs and contribution to the overall value. This helps organizations prioritize resource allocation towards value-enhancing activities.
For instance, in a manufacturing company, the operations activity may be the most crucial since it involves the actual production of goods. However, sales and marketing may also be essential since they contribute to the company's revenue generation. On the other hand, support activities such as infrastructure may not be as critical to the value-creation process.
Step 3: Identify Opportunities for Improvement
In this step, organizations use value chain analysis to identify areas where they can boost efficiency, cut costs, and otherwise extract more value. This helps companies to take corrective measures and optimize their operations.
For example, a manufacturing company may identify that its inbound logistics activity is not functioning efficiently, leading to delays in the delivery of raw materials. By improving this activity, the company can reduce costs and improve its production process.
Step 4: Develop Strategies to Enhance Value Creation
Finally, companies develop strategies to enhance value creation through the optimization of critical value chain activities and the improvement of relationships between different activities. Implementing these strategies enables businesses to remain competitive, efficient, and profitable.
For instance, a manufacturing company may develop a strategy to optimize its operations activity by implementing lean manufacturing techniques. This strategy can help the company reduce waste, improve efficiency, and enhance its value-creation process.
Challenges And Limitations Of Value Chain Analysis
VCA comes hand-in-hand with several challenges and limitations that businesses must overcome to fully reap the benefits.
Data Collection and Analysis
Conducting VCA requires a significant amount of data collection and analysis. Businesses must invest in technology and skilled personnel to gather and analyze this data effectively. The process of data collection and analysis can be time-consuming, and businesses must ensure that the data they collect is accurate and relevant. They must also have the necessary tools and expertise to analyze the data and draw meaningful insights from it.
Moreover, data collection and analysis are ongoing processes, and businesses must continually update their data to reflect changes in their value chains. Failure to do so can lead to inaccurate insights and decisions.
Rapidly Changing Business Environments
The business environment is constantly evolving, with new technologies, changing customer needs, and market disruptors. These changes can make it challenging for businesses to keep up with VCA. Organizations must continually monitor and update their value chains to remain relevant and competitive.
For instance, new technology can disrupt an entire industry, rendering some value-creating activities obsolete. Businesses must be quick to adapt to these changes and restructure their value chains accordingly. Failure to do so can lead to reduced competitiveness and loss of market share.
Overemphasis on Cost Reduction
While cost reduction is vital in VCA, businesses must also focus on value creation. Overemphasis on cost reduction can lead to sacrificing value-creating activities, thereby hindering business growth and long-term sustainability. Businesses must strike a balance between cost reduction and value creation to maximize their benefits from VCA.
For instance, a business may decide to outsource a value-creating activity to a cheaper supplier to reduce costs. However, the quality of the outsourced activity may be inferior, leading to reduced customer satisfaction and loss of market share. Therefore, businesses must carefully evaluate the impact of cost reduction on value creation before making any decisions.
Value Chain Analysis Examples
Now that we've established the ins and outs of VCA, let’s look at some case studies of successful Value Chain Analysis implementation.
Case Study 1: Starbucks
Starbucks, if you aren’t already aware (to the tune of a daily addiction), is a leading coffee chain that has achieved success through its focus on providing high-quality products and services to its customers. The company's value chain analysis reveals that it places emphasis on inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service. Starbucks sources the finest quality coffee beans from producers in Latin America, Africa, and other regions to ensure the best possible product for its customers. It also invests in the latest technology and the skills and knowledge of its employees to deliver an exceptional experience.
In addition to these primary activities, Starbucks has entered into strategic alliances with other organizations to reduce their environmental impact while creating more sustainable practices. This has enabled them to differentiate themselves from their competitors by offering unique customer experiences as well as high-quality beverages.
Overall, Starbucks' value chain analysis reveals that they are committed to providing excellent products and services while also taking steps towards sustainability. By investing in quality ingredients, technology, employee training, and environmental initiatives, they have been able to create a successful business model that sets them apart from their competitors.
Case Study 2: Amazon
Amazon is an excellent example of how effective value chain analysis can be in creating a competitive advantage. By leveraging its strengths in technology, logistics, and customer service, Amazon has been able to reduce costs while increasing efficiency and customer satisfaction. Through the innovative use of data analytics, Amazon has been able to optimize its supply chain operations, raise the industry standard for "fast" delivery times, and improve customer experience. Additionally, Amazon's focus on providing value-added services such as Prime membership and Alexa integration have helped it remain ahead of its competitors. Ultimately, Amazon's success is due in large part to its effective use of value chain analysis to identify areas where it can improve efficiency and create competitive advantages.
Maximizing Value Through Value Chain Analysis
With the tremendous advancements in technology, businesses must adapt and stay ahead of the competition to ensure success. Value Chain Analysis (VCA) is an effective strategy to help enhance value-creation processes, engage stakeholders, and identify opportunities for growth. By following the advice in this guide, you will be able to gain a better understanding of VCA and how it can help your business create long-term value and remain competitive.
As we continue to move into a more digital future, the world is sure to bring new advances that offer even more approaches for businesses looking to maximize their success.
If you liked this article, make sure to subscribe to our newsletter for regular updates.